News
Inefficiencies of ANA Testing
The Journal of Rheumatology has published an analysis of antinuclear antibody (ANA) multiplex testing showing its nonspecific utility and poor rate of return in identifying ANA-associated autoimmune rheumatic disease (ARDs).
Smoking and the Global Burden of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Detailed analysis of the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) 2021 database shows that tobacco and smoking is one of the most significant environmental risk factors for Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) over the last 20 years.
RA leads to ILD: but ILD does not lead to RA
Rheumatoid arthritis is a common autoimmune disease, and approximately 30%-40% of patients develop pulmonary complications such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), but the causal relationship between the two has long been unclear.Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis - NEJM Review
Sandborg et al. has published an overview of juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) - its classification, biology, genetics, , clinical presentations and treatment advances in the New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM).
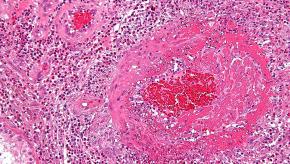
2025 BSR Recommendations for ANCA-associated Vasculitis
The British Society for Rheumatology (BSR) and British Health Professionals in Rheumatology (BHPR) have published a guideline for the management of adults with ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV); specifically three conditions: granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA), microscopic polyangiitis (MPA) and eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA).Rheums Speak - RA Treatment Survey
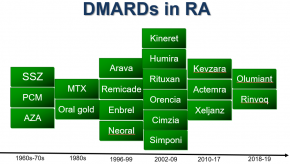
RheumNow's August 2025 “Live Vote” surveys examine Rheumatologist impressions, knowledge and practices over the last 20 years when treating rheumatoid arthritis. The first survey on RA Treatment (7/28/2025) sheds light on evolving prescribing habits, use of biologics, and key frustrations in RA care.Aging Quiets Lupus
A New RA Approval (8.1.2025)
Dr. Jack Cush reviews the news, journal reports and a new treatment for RA from the FDA.