News
Best of 2019 - Biologic Safety Guidelines from the British Society for Rheumatology
In the United Kingdom, NICE has looked to the British Society of Rheumatology (BSR) to develop evidence based guidance on the safe use of biologic DMARDs in patients with inflammatory arthritis.
Best of 2019 - Ups and Downs with Abatacept
Two recent studies have examined the effect of starting abatacept upon the risk of serious hospitalized infections or cancer, showing divergent results from claims data analyses.
Best of 2019 - War on RA - Part 3: Useless Drugs
We have options that are endless – we have 28 biologics in rheumatology; 19 approved for RA in the last 20 years, but 15 of these are me-too copies or biosimilars. We currently have 2 JAK inhibitors and may have 3 or 4 by year end. But what we really need is the right drug, at the right time, in the right patient – but how will we know.Best of 2019 - Are Non-TNF Biologics Superior to TNF inhibitors?
Current ACR and EULAR guidelines list TNF-inhibitors (TNFi) abatacept, rituximab, and tocilizumab as being equally effective after methotrexate or as second line therapies when treating rheumatoid arthritis.
Best of 2019 - Methotrexate and the Risk of Lung Disease
Rheumatology has a comprehensive overview of methotrexate (MTX) and the risk of lung injury, MTX-related pneumonitis and interstitial lung disease (RA-ILD) with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Past reports suggest the frequence of MTX-pneumonitis to be between 0.3 and 11.6%; recent studies suggest it may be much lower.Best of 2019 - SEAM-PsA Study - Does Monotherapy MTX Win Despite Losing to Etanercept in Psoriatic Arthritis?
The SEAM-PsA study examined the efficacy of methotrexate monotherapy, etanercept monotherapy or the combination of MTX and ETN in psoriatic arthritis patients, and found that ETN monotherapy was equivalent to combination therapy - and that both were superior to MTX alone in clinical (ACR and MDA) and radiographic responses.Best of 2019 - The Shame Behind Adalimumab Biosimilars
JAMA has an article this week on the shift from biologic drugs to less expensive therapeutic biosimilar agents. The impact of biosimilars can be easily represented by the shift from adalimuamb - a biologic with nearly $19 billion in sales in 2018 - to any one of the four FDA approved biosimilars for adalimumab (see the daily download for slides on new adalimumab and other biosimilars).Best of 2019 - New EMA Warnings for Tofacitinib in Patients at Risk for Clots
The European Medicines Agency safety committee (PRAC) has concluded that Xeljanz (tofacitinib - TOFA) could increase the risk of blood clots in the lungs and in deep veins in patients who are already at high risk for venous thromboembolic events. The PRAC is recommending that TOFA should be used with caution in patients at high risk of blood clots (VTE), regardless of dose used.Best of 2019 - ACR/SPARTAN Recommendations for the Treatment of Ankylosing Spondylitis and Nonradiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis
The American College of Rheumatology (ACR), in partnership with the Spondylitis Association of America (SAA) and the Spondyloarthritis Research and Treatment Network (SPARTAN), released the 2019 Update of the Recommendations for the Treatment of Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) and Nonradiographic Axi
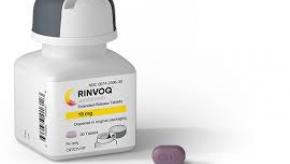
Best of 2019 - Upadacitinib (RINVOQ) FDA Approved for Rheumatoid Arthritis
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on Friday, August 16, approved AbbVie JAK1 inhibitor, Rinvoq (upadacitinib) for adults with rheumatoid arthritis with moderately to severely active disease either not responding to, or intolerant of, methotrexate (MTX).